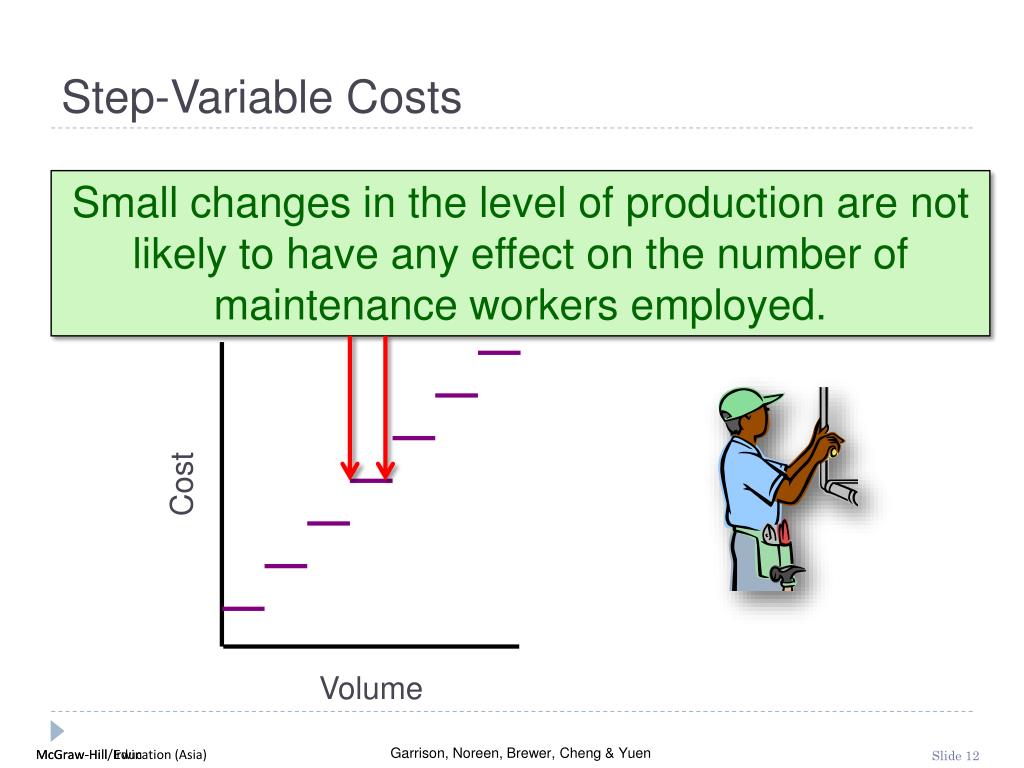
Step cost (or stepped cost) reflects the behavior of the total cost of an operation/ activity at various levels. Step costs are expenses that remain constant for a range of workload. The costs will not fluctuate for a certain range of output, but will abruptly rise or fall after crossing a threshold level.
Fixed versus Variable Costs
Let’s examine Tony’s screen-printing company to illustrate how costs can remain fixed in total but change on a per-unit basis. Now that we have identified the three key types of businesses, let’s identify cost behaviors and apply them to pnl explained faq the business environment. In managerial accounting, different companies use the term cost in different ways depending on how they will use the cost information. Different decisions require different costs classified in different ways.
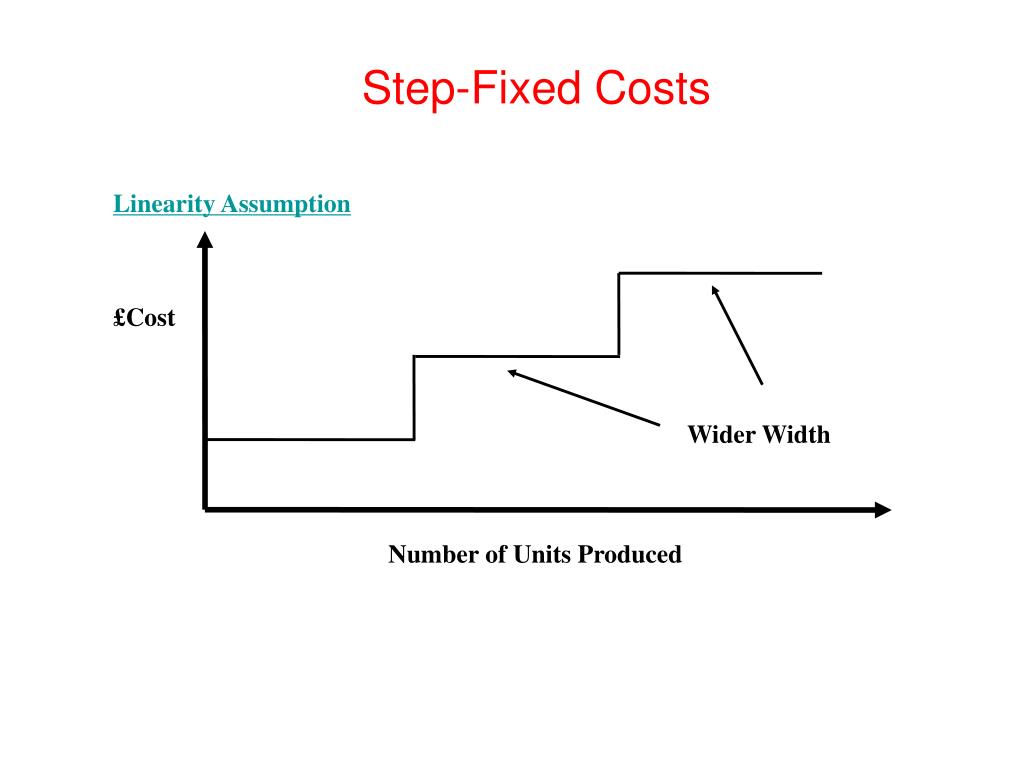
Types of Step Costs
The graph shows that mixed costs are typically both fixed and linear in nature. In other words, they will often have an initial cost, in Ocean Breeze’s case, the $2,000 fixed component of the occupancy tax, and a variable component, the $5 per night occupancy tax. Note that the Ocean Breeze mixed cost graph starts at an initial $2,000 for the fixed component and then increases by $5 for each night their rooms are occupied. Tony operates a screen-printing company, specializing in custom T-shirts. Regardless of whether he produces and sells any T-shirts, he is obligated under his lease to pay $1,000 per month. However, he can consider this fixed cost on a per-unit basis, as shown in Figure 2.15.
Average Fixed Costs versus Average Variable Costs
- Step costs change disproportionately when production levels of a manufacturer, or activity levels of any enterprise, increase or decrease.
- Let us understand the applications of the data interpreted from a step cost graph through the points below.
- The difference between a step-variable cost and a step-fixed cost has to do with the width of the range of activity.
- The $30 cost remains constant whether you create just one user account or three.
- However, sometimes thenature of the work or management policy does not allow direct laborto change as volume changes and direct labor can be a fixedcost.
A high-tech gear manufacturer makes 400 virtual reality headsets in one shift of eight hours with 25 employees and one supervisor. Looking at this analysis, it is clear that, if there is an activity that you think that you cannot afford, it can become less expensive if you are creative in your cost-sharing techniques. Watch the video from Khan Academy that uses the scenario of computer programming to teach fixed, variable, and marginal cost to learn more. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader.
Cost behavior
Step-variable costs behave like fixed costs over a portion of the relevant range and then increase incrementally in a stairstep manner as capacity increases. We are really well exposed to the concept of variable costs that change in the same proportion as the activity level increases. For example, if the activity level increases by 20%, the variable cost increases by 20%. On the contrary, the cost changes disproportionately in the case of step cost. This is because it follows a step pattern, which means it remains constant up to a certain activity level (e.g., production level). Similarly, if the activity level is reduced to a previous level, the cost decreases.
Increase quantum
Committed fixed costs are fixed costs that typically cannot be eliminated if the company is going to continue to function. An example would be the lease of factory equipment for a production company. However, this cost can be converted to a true variable cost by paying employees a fixed amount for each pencil they make, instead of a fixed wage. For example, if the employee is paid 10 cents for each pencil he or she makes, the labor cost is now a true variable cost. Stepped cost refers to the behavior of the total cost of an activity at various levels of the activity.
When labor costs are incurred but are not directly involved in the active conversion of materials into finished products, they are classified as indirect labor costs. For example, Carolina Yachts has production supervisors who oversee the manufacturing process but do not actively participate in the construction of the boats. Their wages generally support the production process but cannot be traced back to a single unit. For this reason, the production supervisors’ salary would be classified as indirect labor. However, if you are considering the supervisor’s salary cost on a per unit of production basis, then it could be considered a variable cost. Many businesses can make decisions by dividing their costs into fixed and variable costs, but there are some business decisions that require grouping costs differently.
Unavoidable fixed costs are costs you have to incur if you want to stay in business. For example, the administrative costs of running a processing facility are an unavoidable fixed cost. Interest on term debt on the facility is also an unavoidable fixed cost. Step costs are also known as stair-step costs or often as step-variable cost or a step-fixed cost. The costs that do change as the number of participants change are the variable costs.

